Electric Vehicle Charging in South East England
Table of Contents
About EV Charging
Electrical car (EV) charging is a significant element of EV ownership with the power rating, type of connector, cable specifications and car specification to be considered. There are three primary kinds of EV charging–quick, quick and slow. They depict the energy outputs, and therefore the charging speeds, which are accessible for charging the EV. Note that the energy is measured by kilowatts (kW).
Rapid chargers are one of two kinds–AC or DC. Current AC chargers are rated at 43 kW, while most DC units are rated at least 50 kW. Both supply the majority of EVs at 80 per cent in about 30-60 minutes (depending on the ability of the battery). Tesla Superchargers are also fast DC and charge at around 120 kW. The Rapid AC systems are fitted with a Type 2 tethered connector, and the Rapid DC chargers are equipped with CCS, CHAdeMO or Tesla Type 2.
Slow units (up to 3 kW) are best used for charging your vehicle overnight and generally take between 6 and 12 hours for a pure EV or 2-4 hours for a PHEV. EVs, pay for slow systems utilizing a cable that connects the car to a 3-pin or Type 2 socket.
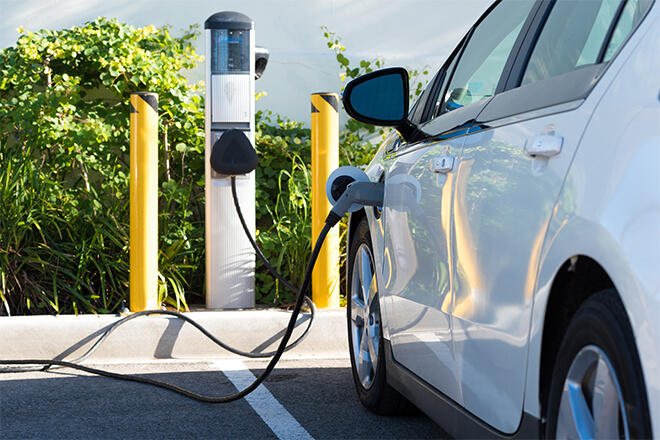

Electric cars are all equipped with a 120 volt charging cable that can charge the battery from the household socket if there are no other options.
But sooner or later, most electric car owners will want a 240 volt Level 2 charging station that can recharge the vehicle as much as four times quicker.
Owners of plug-in hybrid vehicles with ranges below 30 miles may find the conventional charging cable okay, but as plug-in ranges rise, they too may decide that the charging station will boost their all-electric drive.
Level 2 charging stations use a 240-volt scheme (comparable to a clothes dryer plug) and can fully charge a car with a 0 per cent charge in approximately four to six hours.
Our Guarantee
- Over Six years experience
- Unrivaled experience
- An exceptional service
- Unbeatable value for money
- Industry-approved installers
- A full range of electrical services
- Professional, reliable and diligent
- 100% safety and satisfaction
EV Charging explained
We are developers funders and installers of quick EV chargers offering EV charging alternatives for high-density residential development of landowners and corporate estate managers.
These government chargers are often situated near restaurants, shopping centres, parking places and public spaces.
Ideal where quick turnaround is needed, fast chargers charge a battery of 40 kW to 80 in 30 minutes via DC or AC supply.
These charging points will securely charge the car at a speed that is appropriate to the power supply.
What’s the Smart Charging?
Load Balancing distributes the available ability in proportion to all active charging stations.
Load Balancing ensures that all-electric cars are optimally charged at your place within the limits of the capacity of your charging stations.
How quickly can you charge an electric car at home?
Home charging points charge your car at 3.7kW or 7kW, offering approximately 15-30 miles per hour of charge (compared to 2.3kW from a three-pin socket offering up to 8 miles of range per hour).
Modes of Charging
There are four main modes (as described in BS EN 61851 1) for charging an electric vehicle as summarized below.
- Mode 1 should not be used for charging an electric vehicle because RCD protection required for a safe charging system can not be guaranteed at all outlets.
- Mode 2 wires are given with a cable control box (including an RCD) set and adapted to the particular charging power and ensure that RCD protection is supplied during charging.
- Mode 3 consists of the Electric Vehicle Supply Facility (EVSE) which guarantees the protection and control features of the chargers.
- Mode 4 is a required service feature for fast charging for use as roadside assistance and service station charging for lengthy trips.
Home Charging
Home chargers can be installed for private individuals living in detached or semi-detached housing. Charging your vehicle at home is often the most convenient and cost-effective way for private clients to recharge their cars because most cars are parked overnight.
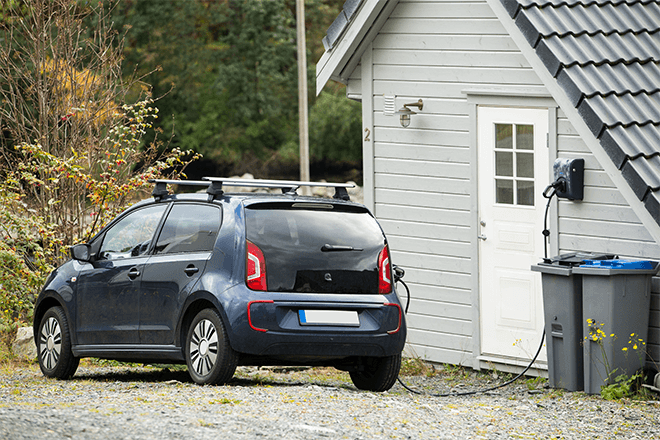
Most individuals choose to install Level 2 charging in their garage, but stations can also be installed outside and are even secure to use when it rains.
Level II chargers involve a 240-volt outlet (the same type as your clothes dryer) and may include the installation by an electrician.
About Mittens Electrical
Trust
Happy clients mean we receive lots of positive word of mouth recommendations, which also means our partners’ reputations are under scrutiny when we act on their introductions. Our willingness to share our expertise and product knowledge within our partners’ organisations helps create a mutually beneficial working relationships and reciprocates that trust.
Our History
Established in 1935, a small family engineering firm has evolved into a successful multi million pound business, providing a wide range of products and services to local enterprises and large multi nationals alike. Every client enjoys and benefits from the same focused delivery approach ensuring that each and every job is completed to the highest standards
Reputation
We pay attention to detail. Our proven industry-leading expertise and strong focus on safety, regulation and accreditation are all key factors when choosing Mittens Electrical. Clients often invite us to get involved early in their project design to help minimise costly design oversights.
Quality
With over 80 years experience of delivering quality service and solutions to our clients, we always seek to enhance not just our reputation, but our partners’ too. Service and quality underpin everything that we do. Experience counts.
we can help on your next project
Grants for Electric Vehicle Charging
If you’re going to charge your car regularly at home, installing an authorized home charger is the fastest and safest way to charge your car–and comes with a Government grant of up to £500 for installation costs.
EV Charging Cost
The price of a Level 2 electric vehicle charger designed for a single user can range from £400 to £4,000 based on the factors involved, including the complexity of the building modifications required to provide the link between the charger and the electrical panel.
The scheme may also price distant energy from congested energy fields differently and enable credit card and money payments to the PMS user interface terminal.
Furthermore, such a charging station can direct energy gathered via solar panels back to the grid or storage car based on market prices obtained wirelessly or via the internet.
Such energy can be shifted to local storage in 205 or transferred back to grid 206 alternately to electricity produced by solar panels in 2011 or other sources, which can be stored and then moved to the grid or vehicle 200 based on internet or wireless network rates or communications.
The home charging point, fully mounted, is worth GBP 279 with the government grant.
• Once mounted, you will only pay for the energy you use to charge.
• The average electricity level in the United Kingdom is around 14p per kWh, while for Economy 7, the average overnight energy level in the United Kingdom is 8p per kWh.
Statistics
The Government offers economic assistance for customers to install a charging point in their home premises under the Electric Vehicle Home Charge Scheme (EVHS), which will cover up to 75% of the total expenses.
The grant is set as a 75 per cent contribution to the cost of one charging point and its installation and is capped at £ 500 Charging time is decreased by 30-60 per cent depending on the vehicle, making charging at home much faster.
Driven by the need to decrease emissions of CO2 by at least 80% by 2050, the United Kingdom is starting to follow suit.
In his Autumn Statement, Chancellor Philip Hammond announced on-the-job charging grants and 100% first-year capital allowances for on-the-job charging.
In just three years, electric cars are projected to account for up to 10% of all new vehicle sales. (startups.co.uk) The Electric Vehicle Homecharge Scheme (EVHS) grants up to 75% of the price of installing charging points for electric vehicles at national estates across the United Kingdom.
Electric car owners residing in an estimated 43% of homes that do not have access to off-street parking may well look to retailers and employers to provide a solution to their charging requirements.
Are you in need of a professional electrician?
